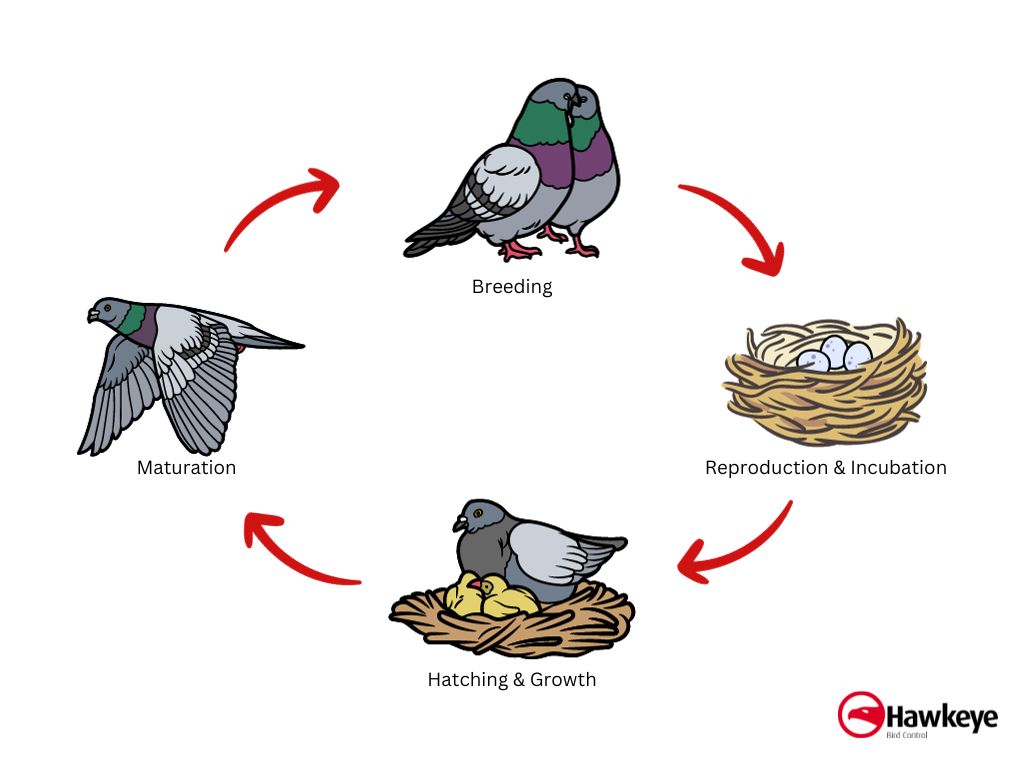
Lifespan of Pigeon Bird: Secrets to Pigeons Survival
The lifespan of a pigeon typically ranges from 3 to 15 years. Factors like species, environment, and care can influence their longevity.
Pigeons are fascinating birds known for their adaptability and intelligence. Often found in urban areas, they have become symbols of peace and love. Their social nature allows them to thrive in flocks, making them a common sight in parks and streets.
Pigeons can be domesticated or wild, each with unique traits and behaviors. Understanding their lifespan is crucial for bird enthusiasts and pet owners alike. Proper care, nutrition, and a safe environment can significantly impact how long these birds live. This article explores the factors affecting pigeon lifespan and offers insights into their care and management.
Introduction To Pigeon Lifespan

Credit: www.aejames.com
Pigeons are fascinating birds found all over the world. Their lifespan varies based on many factors. Understanding how long these birds live helps us appreciate their role in nature.
Typical Lifespan In The Wild
In the wild, pigeons typically live between 3 to 5 years. This shorter lifespan is due to various dangers.
- Predators like hawks and cats
- Diseases and parasites
- Food scarcity during harsh weather
Despite these challenges, some pigeons can live longer. A few may reach up to 15 years in safe environments.
Lifespan Variations Among Species
Different pigeon species show varying lifespans. Here’s a quick look:
| Species | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Rock Pigeon | 3-5 years |
| Feral Pigeon | 5-15 years |
| Victoria Crowned Pigeon | 15-20 years |
| Nicobar Pigeon | 10-15 years |
Each species has unique traits affecting its lifespan. Factors include habitat, diet, and health.
Factors Influencing Pigeon Longevity
The lifespan of pigeons varies widely. Many factors contribute to how long they live. Understanding these factors helps in caring for these birds.
Genetics And Species Characteristics
Genetics play a vital role in a pigeon’s lifespan. Different pigeon species have different lifespans.
- Wild Pigeons: Average lifespan is 3-5 years.
- Domestic Pigeons: Can live up to 15 years or more.
- Racing Homers: Some live over 20 years.
Health traits also vary among species. Some pigeons are more resistant to diseases. Stronger genetics lead to better health and longer life.
Impact Of Urban Environments
Urban settings greatly affect pigeon longevity. Many challenges exist in cities.
| Challenge | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Pollution | Reduces health, leading to shorter life. |
| Food Availability | May lead to malnutrition. |
| Predators | Increased risk of attacks. |
| Traffic | Higher risk of accidents. |
Despite these challenges, some urban pigeons adapt well. They find food and shelter, helping them survive.
Understanding these factors helps in creating a better environment for pigeons.
Adaptations For Urban Survival
Pigeons have unique traits that help them thrive in cities. They adapt quickly to urban life. These adaptations include their diet and nesting habits.
Dietary Flexibility
Pigeons are known for their dietary flexibility. They can eat various foods found in urban areas. This includes:
- Seeds
- Fruits
- Human food scraps
This ability to consume different foods helps them survive. They can find nourishment in parks, streets, and rooftops. Their digestive systems are also adaptable. They can efficiently process diverse food sources.
Nesting In Human Structures
Pigeons utilize human-made structures for nesting. Buildings, bridges, and ledges provide safe spots. This choice protects them from predators. Common nesting sites include:
| Location | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Building rooftops | High elevation, safety from ground predators |
| Bridges | Stable structures, reduced disturbance |
| Balconies | Close to food sources, sheltered |
Pigeons often use materials like twigs, paper, and plastic for their nests. These materials are easy to find. Nesting in urban areas ensures their survival.
Health Challenges And Predators
Pigeons face many health challenges and threats in urban environments. Understanding these issues helps in protecting them. Their lifespan can be greatly affected by diseases and predators.
Common Diseases
Pigeons can suffer from various diseases. Here are some common ones:
- Paramyxovirus: Affects the nervous system.
- Coccidiosis: Affects the intestinal tract.
- Psittacosis: A bacterial infection that can spread to humans.
- Newcastle disease: Causes respiratory issues.
- Trichomoniasis: Affects the throat and digestive system.
Regular health checks can prevent these diseases. Vaccination is important for disease control.
Natural Predators In Cities
Pigeons have many natural predators in urban settings. Here are some common ones:
| Predator | Details |
|---|---|
| Hawks | Fast and agile, they hunt pigeons easily. |
| Falcons | Known for their speed and precision. |
| Cats | Domestic cats can be a significant threat. |
| Dogs | Roaming dogs may chase and catch pigeons. |
Understanding these predators helps in creating safer environments for pigeons. Urban planning can make a difference.
Human Impact On Pigeon Lifespan
Humans greatly influence the lifespan of pigeons. Activities like urbanization, pollution, and hunting affect their health and survival. Understanding these impacts helps in their conservation.
Feeding Habits
Feeding habits play a crucial role in the life of pigeons. Urban environments offer different food sources compared to rural areas. Here are some key points:
- Urban pigeons often eat leftover human food.
- Natural diets include seeds, fruits, and grains.
- Unhealthy foods can lead to diseases.
- Natural foraging promotes better health.
Improper feeding can shorten their lifespan. Healthy diets allow pigeons to thrive. Education about proper feeding helps protect them.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aim to improve pigeon lifespans. Various organizations work to protect their habitats. Here are some effective strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat Restoration | Restoring natural habitats supports pigeon populations. |
| Public Awareness | Educating communities helps reduce harm to pigeons. |
| Research Programs | Studying pigeon behavior aids in better conservation. |
These efforts help ensure a longer lifespan for pigeons. Protecting them benefits the ecosystem. Every action counts in their survival.
The Role Of Pigeons In Ecosystems
Pigeons play a vital role in our ecosystems. They help maintain balance in nature. Understanding their contributions is important for appreciating these birds.
Seed Dispersal
Pigeons are excellent seed dispersers. They eat fruits and seeds from various plants. After digestion, they excrete seeds far from the parent plant. This helps in:
- Spreading plant species
- Increasing plant diversity
- Promoting healthy ecosystems
Studies show that pigeons can travel long distances. They often visit urban parks and green spaces. This behavior supports plant growth in city areas.
Prey For Urban Predators
Pigeons serve as prey for many urban predators. Birds of prey like hawks and falcons hunt them. Other animals, such as cats and foxes, also rely on pigeons for food.
This relationship helps control pigeon populations. It creates a balanced food web in urban settings. Without pigeons, these predators might struggle to survive.
Here’s a table showing common urban predators of pigeons:
| Predator | Hunting Method |
|---|---|
| Hawk | Soaring and diving |
| Falcon | Speedy dives |
| Cat | Stalking and ambushing |
| Fox | Chasing and pouncing |
Research And Studies On Pigeon Aging
Understanding the lifespan of pigeons requires scientific research. Studies focus on various aspects of their aging process. Researchers explore how factors like diet, environment, and genetics affect their life expectancy. This section covers the scientific methods and key findings on pigeon aging.
Scientific Methods
Researchers use several scientific methods to study pigeon aging:
- Longitudinal Studies: Tracking pigeons over many years.
- Genetic Analysis: Examining DNA to understand hereditary factors.
- Behavioral Observations: Noting changes in behavior as pigeons age.
- Health Assessments: Regular check-ups to monitor health status.
These methods help scientists gather accurate data. They provide insights into how pigeons age in different conditions.
Key Findings
Research reveals several important findings about pigeon aging:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Diet | Balanced diets lead to longer lifespans. |
| Environment | Safe, clean habitats increase longevity. |
| Genetics | Some breeds live longer than others. |
| Healthcare | Regular vet visits improve health and lifespan. |
Key findings show that pigeons can live up to 15 years. Proper care and environment greatly influence their lifespan. The oldest recorded pigeon lived for 32 years. Research emphasizes the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
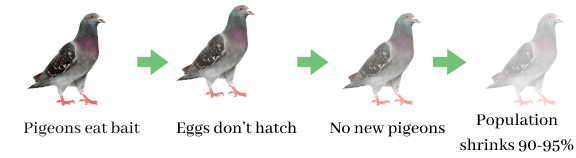
Credit: www.ovocontrol.com
Conservation And The Future of Urban Pigeons
Urban pigeons play a vital role in city ecosystems. Their presence offers many benefits. Conservation efforts are essential for their survival. Understanding how to protect them ensures a healthy future.
Protective Measures
Implementing protective measures is crucial for urban pigeons. These measures help maintain their population and health. Here are some effective strategies:
- Safe nesting sites: Provide safe spaces for pigeons to nest.
- Feeding programs: Establish community feeding stations with healthy food.
- Humane population control: Use methods like egg replacement instead of culling.
- Public education: Teach people about the benefits of pigeons.
These actions can create a supportive environment for pigeons. They help pigeons thrive in urban settings.
Community Involvement
Community involvement is key to pigeon conservation. Engaged citizens can make a significant difference. Here’s how communities can help:
- Volunteer programs: Organize groups to clean up urban areas.
- Adopt-a-Pigeon: Encourage people to care for local pigeons.
- Workshops: Host events to educate the public about pigeons.
- Art projects: Create murals or installations celebrating pigeons.
Engaging the community fosters a sense of responsibility. People will feel connected to urban wildlife.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Safe nesting sites | Provide secure locations for pigeons to raise their young. |
| Feeding programs | Establish designated areas for healthy pigeon feeding. |
| Public education | Inform the public about the importance of urban pigeons. |
Together, these efforts will enhance the future of urban pigeons. A collaborative approach leads to a thriving ecosystem.

Credit: www.newyorker.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Average Lifespan Of A Pigeon?
Pigeons typically live between 5 to 15 years in the wild, depending on environmental factors and predation.
Can Pigeons Live Longer In Captivity?
Yes, captive pigeons can live up to 20 years with proper care, nutrition, and a safe environment.
What Factors Affect A Pigeon’s Lifespan?
Predation, disease, diet, and habitat quality significantly influence the lifespan of pigeons.
Do Different Pigeon Breeds Have Varying Lifespans?
Yes, some breeds may have longer lifespans due to genetic factors and specific care requirements.
How long do pigeons live?
Pigeons typically live between 3 to 5 years in the wild. However, with proper care, they can live much longer in captivity. Some pigeons reach 15 years or more when kept as pets. Their lifespan often depends on their environment and health. Pigeons face many dangers in the wild, including predators and disease.
In a safe home, they receive regular food, water, and veterinary care, which helps them thrive. Taking good care of these birds can lead to longer, happier lives.