Difference between Chicken, Hen, and Rooster
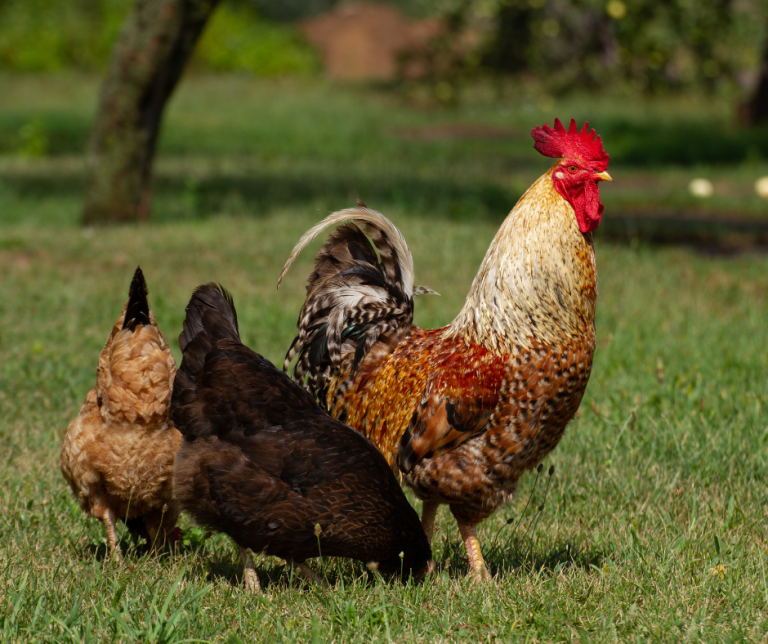
Chicken refers to the species as a whole, while a hen is a female chicken, and a rooster is a male. Hens lay eggs, whereas roosters are known for their crowing and mating behavior.
Understanding the differences between chickens, hens, and roosters is essential for poultry enthusiasts and farmers alike. Chickens are domesticated birds that provide meat and eggs, forming a vital part of agriculture worldwide. Hens contribute significantly by laying eggs, which are a staple food source for many cultures.
Roosters, on the other hand, play a crucial role in breeding and maintaining flock dynamics. Knowing these distinctions helps in managing poultry effectively. This knowledge is beneficial not only for farming practices but also for making informed choices in culinary uses and animal husbandry.

Credit: www.kalmbachfeeds.com
Introduction To Poultry Terminology
Understanding poultry terms is important for everyone. Many people confuse chickens, hens, and roosters. A chicken refers to the species as a whole. Both hens and roosters are types of chickens. Hens are female chickens that lay eggs. Roosters are male chickens known for their crowing.
Some think all chickens are hens. This is incorrect. Roosters play a different role on a farm. They protect the flock and help with breeding. Using the correct terms helps avoid confusion.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Chicken | General term for the species. |
| Hen | Female chicken that lays eggs. |
| Rooster | Male chicken known for crowing. |
Chicken: The General Term
Chicken is a general term used for all domesticated birds. It includes both hens and roosters. Hens are female chickens, while roosters are male. Chickens belong to the species Gallus gallus domesticus.
Chickens play an important role in agriculture. They provide meat and eggs for human consumption. Hens lay eggs regularly, making them valuable for farms. Roosters help fertilize these eggs.
In many diets around the world, chicken is a key protein source. It is versatile and can be cooked in many ways. Chicken dishes are popular in various cuisines.
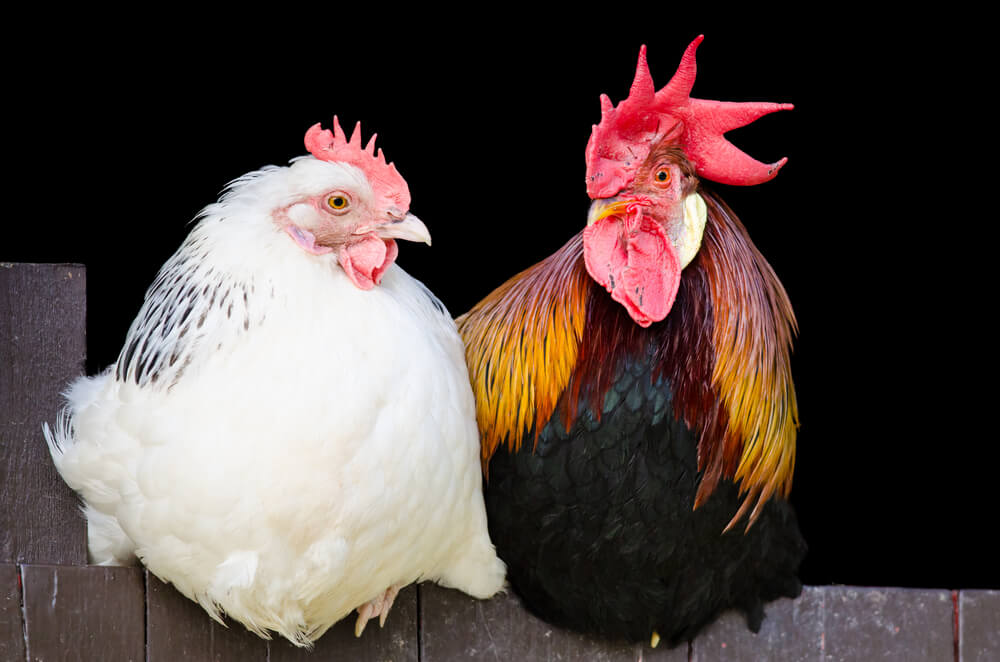
Hen: The Female Of The Species
A hen is a female chicken. She plays a vital role in the flock. Hens are known for their friendly and nurturing behavior. They often gather in groups and enjoy socializing.
Characteristics of hens include a calm demeanor and protective instincts. They can lay eggs regularly, especially when well-cared for. A healthy hen lays about 250-300 eggs per year. Egg production can depend on age, breed, and environment.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Age | Hens typically start laying eggs at 5-6 months old. |
| Breed | Some breeds are better egg producers than others. |
| Environment | A safe and clean space boosts egg production. |

Credit: moreaboutchicken.com
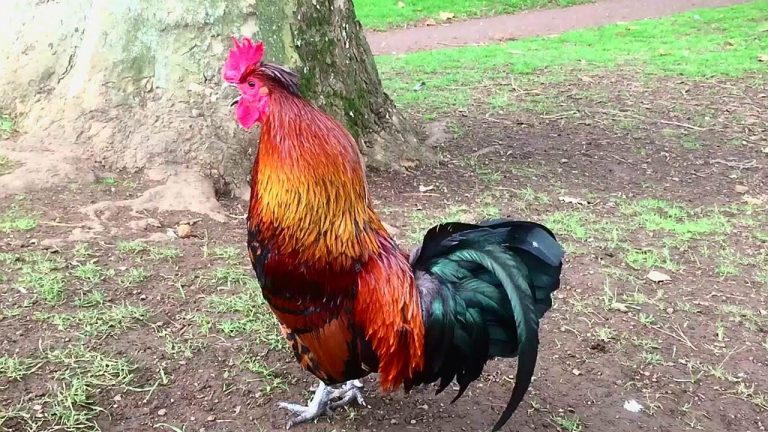
Rooster: The Male Counterpart
A rooster is the male chicken. It has striking physical features. Roosters often have bright feathers, a distinctive comb, and a long tail. These traits make them stand out in the flock.
Roosters play an important role in a flock. They are known for their protective behavior. A rooster watches over hens and warns them of danger. They also help establish pecking order within the group.
Roosters are often more vocal than hens. Their crowing signals the start of a new day. This behavior can also attract hens for mating.
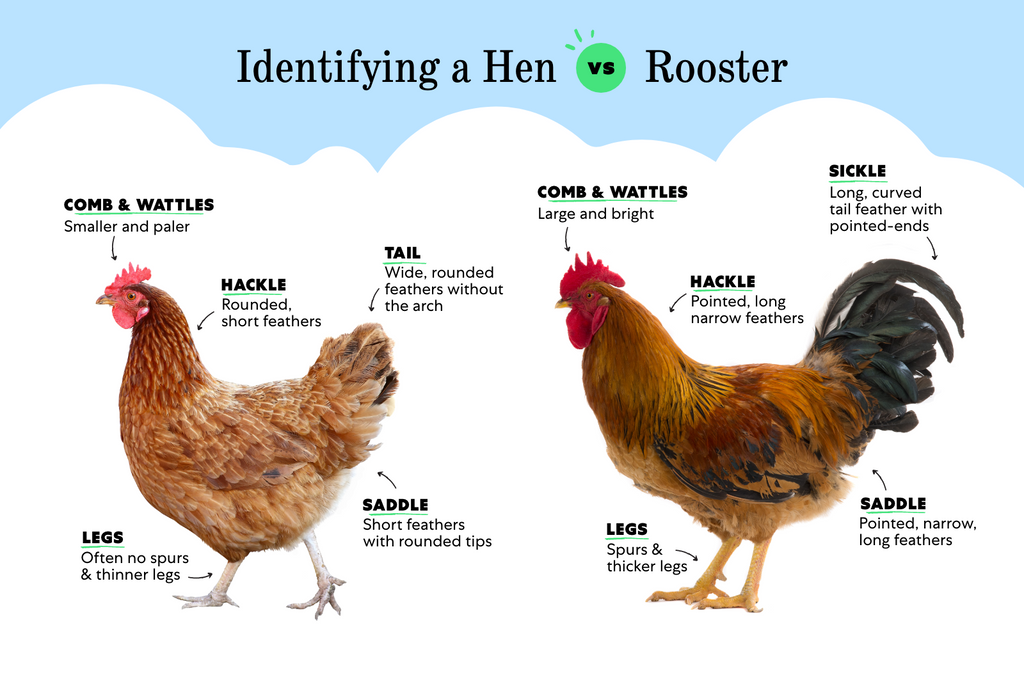
Anatomical And Behavioral Differences
The chicken is a general term for domesticated birds. A hen is a female chicken. A rooster is a male chicken. Each has distinct physical traits.
Hens have a rounder body and smaller combs. Roosters display bright feathers and larger combs. Chickens come in different colors and sizes. Their feathers can be white, brown, or black.
Behavior also varies between these birds. Hens often cluck softly while foraging. Roosters crow loudly to mark territory. Hens are nurturing and care for their chicks. Roosters protect the flock from danger.

Credit: modernfarmer.com
Impact On Farming Practices
Breeding practices vary significantly between chickens, hens, and roosters. Farmers focus on specific traits for better egg production or meat quality. Hens are often kept for their eggs, while roosters are essential for fertilization.
Population control is crucial in farming. Farmers manage the number of hens and roosters to ensure healthy growth. Too many roosters can lead to fighting and stress among hens.
Economic considerations affect farming choices. Keeping hens generally costs less than raising roosters. Hens provide a steady supply of eggs, which can lead to higher profits.
Roosters may be necessary for breeding, but they do not produce eggs. Understanding the roles of each bird helps farmers maximize efficiency and profitability.
Cultural And Symbolic Significance
Chickens, hens, and roosters hold rich cultural and symbolic significance. Many myths feature these birds as symbols of fertility and prosperity. In various cultures, roosters are seen as guardians of the dawn. They symbolize awakening and new beginnings.
Hens often represent nurturing and motherhood. They are seen as caring figures in many folktales. In some traditions, they symbolize sacrifice and protection of the family. Chickens are often associated with abundance and harvest.
Modern symbolism also varies. Roosters are used in art and decor to symbolize bravery. Hens are often seen in kitchen themes, representing comfort and home. Overall, these birds carry deep meanings across cultures.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between chickens, hens, and roosters is essential for anyone interested in poultry. Each plays a unique role in farming and daily life. Knowing these distinctions can enhance your appreciation for these birds. Whether for farming or as pets, recognizing their characteristics enriches your experience with them.