Can You Eat Pigeon Eggs | It is Edible And Safe?
You can eat pigeon eggs. Pigeon eggs are safe for consumption and are similar in taste and nutritional value to chicken eggs. Simply cook them like you would any other eggs—boil, fry, or scramble them. However, keep in mind that collecting pigeon eggs from the wild is not recommended due to potential contamination. It’s better to obtain them from a reliable source.
Are Pigeon Eggs Edible?
Pigeon eggs are edible. You can eat them just like chicken eggs. Pigeon eggs are commonly consumed in some cultures and are considered a delicacy. They can be boiled, fried, or used in various recipes. Just make sure to cook them thoroughly before eating to ensure they are safe to consume.
Is It Safe to Eat Pigeon Eggs?
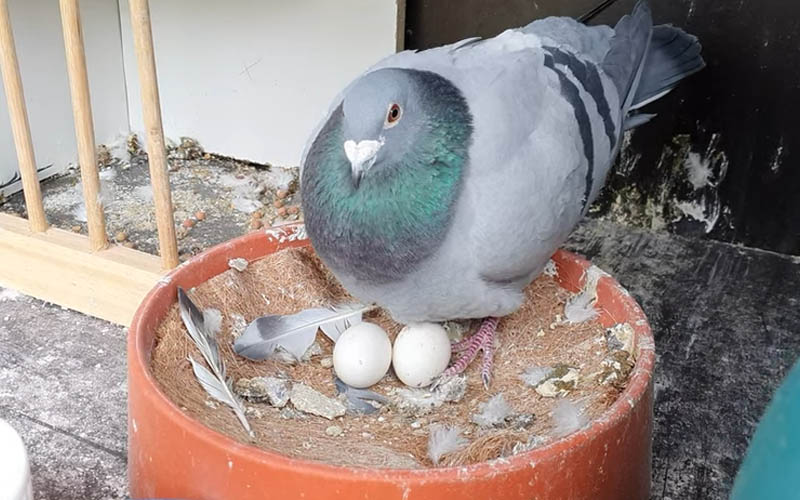

Eating pigeon eggs is generally safe. Pigeon eggs are consumed in many cultures and are considered a nutritious source of protein and essential nutrients. Ensure they are properly cooked to minimize any potential risks. Cooking eggs thoroughly helps eliminate harmful bacteria, making them safe for consumption. Just like chicken eggs, pigeon eggs are a wholesome and safe addition to your diet when prepared correctly.
Where Can You Find Pigeon Eggs?
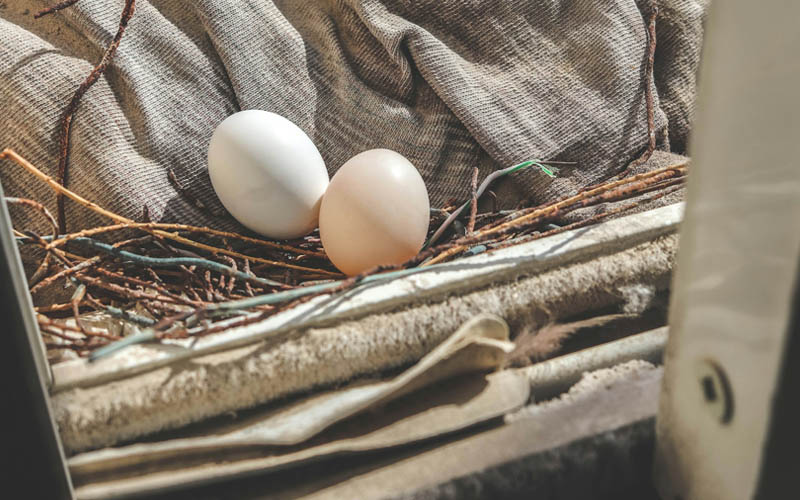

Pigeon eggs can typically be found in nests built by pigeons. Pigeons are known to build nests in various locations, such as on building ledges, in trees, on windowsills, and even in sheltered areas on balconies or rooftops. The exact location can vary depending on the species of pigeon and the environment they inhabit.
It’s important to note that disturbing or removing pigeon eggs may not be legal in some areas, as pigeons are often protected by animal welfare laws. If you have concerns about pigeons or their eggs in a specific location, it’s advisable to contact local animal control or wildlife authorities for guidance on appropriate actions.
Can You Eat Pigeon Eggs Raw?
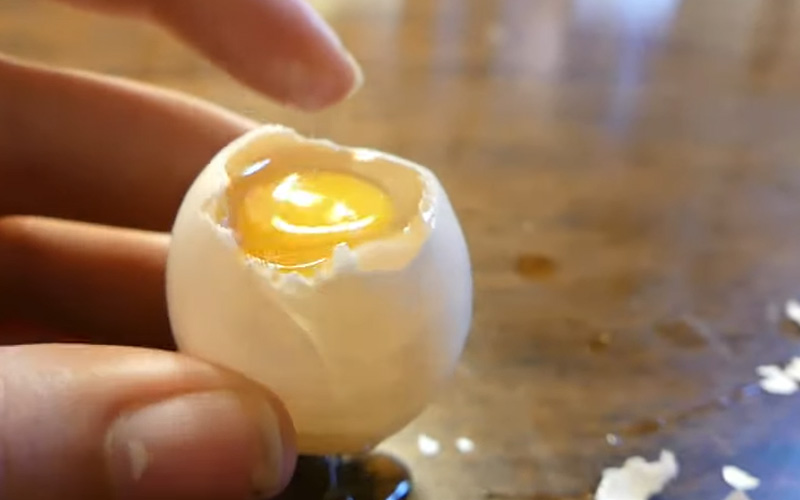

It’s generally not recommended to consume raw eggs of any kind, including pigeon eggs, due to the risk of bacterial contamination such as Salmonella. Raw eggs can potentially contain harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. It’s safer to cook eggs thoroughly before consuming them to reduce the risk of foodborne illness. Cooking eggs until both the whites and yolks are firm is the best way to ensure they are safe to eat.
What Do Pigeon Eggs Taste Like?
Pigeon eggs are said to have a flavor similar to chicken eggs but with a richer and creamier taste. Some people describe them as having a slightly gamey or earthy flavor, and the yolk is often considered more flavorful than that of a chicken egg. However, taste can be subjective, and individual preferences may vary. Keep in mind that pigeon eggs are not as widely consumed as chicken eggs, so they may be more challenging to find and are often considered a delicacy in some cultures. If you have the opportunity to try pigeon eggs, it’s recommended to cook them in a way that allows you to appreciate their unique taste.
Pigeon Egg Nutritional Value:

Pigeon eggs, like those of many other birds, are a good source of nutrition. However, it’s important to note that pigeon eggs are not as commonly consumed as chicken eggs, and specific nutritional information may not be as readily available. In general, bird eggs are a good source of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Here are some common nutritional components found in bird eggs, including pigeon eggs:
- Protein: Eggs, including pigeon eggs, are rich in high-quality protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body.
- Fats: Eggs contain both saturated and unsaturated fats. They are a good source of healthy fats, including omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Vitamins: Eggs are a good source of various vitamins, including vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and B-complex vitamins. These vitamins play crucial roles in maintaining overall health.
- Minerals: Pigeon eggs, like other bird eggs, contain essential minerals such as iron, phosphorus, and selenium, which contribute to various bodily functions.
- Cholesterol: Eggs, including pigeon eggs, are known for their cholesterol content. While they contain cholesterol, research suggests that dietary cholesterol may not have as significant an impact on blood cholesterol levels as once thought.
A table detailing the nutritional profile of pigeon eggs per 100 grams:
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 158 kcal |
| Protein | 13.6 g |
| Fat | 11.0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 1.1 g |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Sugars | 1.1 g |
| Calcium | 53 mg |
| Iron | 3.1 mg |
| Magnesium | 11 mg |
| Phosphorus | 240 mg |
| Potassium | 123 mg |
| Sodium | 141 mg |
| Zinc | 1.1 mg |
| Vitamin C | 0 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.3 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.4 µg |
| Vitamin A | 416 IU |
| Vitamin D | 0 µg |
| Vitamin E | 1.1 mg |
| Vitamin K | 0.1 µg |
| Folate | 47 µg |
| Choline | 283 mg |
Pigeon Egg Benefits:
Pigeon eggs, like other bird eggs, offer various nutritional benefits. While they are not as commonly consumed as chicken eggs, they do provide a good source of essential nutrients. Here are some potential benefits of pigeon eggs:
- Protein: Pigeon eggs are rich in high-quality protein, which is crucial for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Pigeon eggs contain essential vitamins such as B vitamins (including B12) and minerals like iron, phosphorus, and selenium. These nutrients play key roles in various bodily functions, including energy production, bone health, and immune system support.
- Cholesterol: While pigeon eggs do contain cholesterol, they also have a favorable balance of healthy fats. Some studies suggest that moderate egg consumption may not significantly impact cholesterol levels in the blood for most people.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Pigeon eggs, like other bird eggs, contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are important for heart health and can contribute to a well-balanced diet.
- Amino Acids: Eggs, including pigeon eggs, provide essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. These amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, contributing to the body’s overall protein synthesis.
- Choline: Pigeon eggs are a good source of choline, a nutrient important for brain health, liver function, and metabolism.
Pigeon Egg Side Effects:
There isn’t much information available specifically on the side effects of consuming pigeon eggs. Pigeon eggs are generally considered safe to eat for most people when cooked thoroughly, similar to chicken eggs. However, it’s crucial to keep in mind a few general considerations:
- Allergies: Some individuals may be allergic to eggs in general, and this could apply to pigeon eggs as well. Allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms like itching and hives to more severe reactions like difficulty breathing. If you have egg allergies, it’s advisable to avoid pigeon eggs.
- Contamination: As with any type of egg, there is a risk of contamination with bacteria such as Salmonella. Cooking eggs thoroughly helps reduce this risk. Ensure that the eggs are stored properly and cooked to a safe temperature.
- Cholesterol: Like chicken eggs, pigeon eggs contain cholesterol. While moderate egg consumption is generally considered part of a healthy diet for most people, those with specific health concerns like high cholesterol levels may need to monitor their intake.
- Nutrient Sensitivity: Some individuals might have specific sensitivities to certain nutrients found in eggs, such as biotin or choline. However, this is not common, and most people can consume eggs without any issues.
FAQ
Chicken eggs are generally considered better than pigeon eggs. Chicken eggs are larger, more widely available, and richer in nutrients like protein and vitamins. Pigeon eggs are smaller and less commonly consumed, making them less practical for regular consumption.
Historically, there have been notable dishes featuring pigeon eggs. One famous example is the “Nest of the Phoenix,” a Chinese delicacy where pigeon eggs are carefully cooked and served in a nest-like arrangement. This dish has been enjoyed for centuries and remains a symbol of culinary craftsmanship in Chinese cuisine.
It is generally safe to eat bird eggs, as long as they are properly cooked. Cooking eggs thoroughly kills harmful bacteria and reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses. Ensure eggs are from reputable sources, stored correctly, and cooked until both the white and yolk are firm.
Pigeons can carry diseases. These birds may harbor harmful germs and parasites. Contact with their droppings or feathers can lead to health risks. It’s essential to be cautious, especially in areas with high pigeon populations, to prevent potential infections and maintain personal hygiene.